Together, the people of Massachusetts can build a better Commonwealth, one that advances both economic and racial justice. We can transform our communities by addressing the backlog of crumbling roads, bridges, and public transit systems. We can replace aging schools with modern buildings, ones that are well-resourced, both with supplies and staff. We can provide affordable, high-quality childcare and put vocational training and higher education within reach of those who want it. Major investments like these will propel our people and our communities forward.
When making these investments, it is especially important that lawmakers prioritize the needs of Black, brown and Latinx communities. Due to a centuries-long history of systemic racism, these groups have much lower average household incomes and continue to face obstacles to economic opportunity. This is an injustice we can and must correct.
To achieve this vision, we will need to collect substantial, additional tax revenue – and we’ll need to do that in a way that’s fair. An added tax on household income above $1 million a year would make these transformative, ongoing investments possible and would be paid for by the few, very highest income households in the state. These are the same households that benefit from billions of dollars each year in state and federal tax breaks. These households have prospered during the pandemic, even while most Massachusetts families continue to struggle. Such a tax (often called a “millionaire tax”) would affect less than one percent of households – fewer than seven in every thousand families. And the tax would apply only to the portion of their annual income above $1 million. Importantly for racial justice, these few, very high-income households are disproportionately white.
A millionaire tax would advance economic and racial justice in Massachusetts, both in the way the tax is collected – from very high-income households, which are predominantly white – and through the ongoing investments it would make possible.
Very high-income, white households would pay large majority of millionaire tax
In Massachusetts, white households would contribute the great majority of the revenue that would be collected through an added tax (or “surtax”) applied to income above $1 million a year. As the pie chart below shows, in Massachusetts, 86 percent of households with annual income above $1 million are white. These white households would pay, at a minimum, about 86 of every 100 dollars of the tax revenue collected from a millionaire tax.
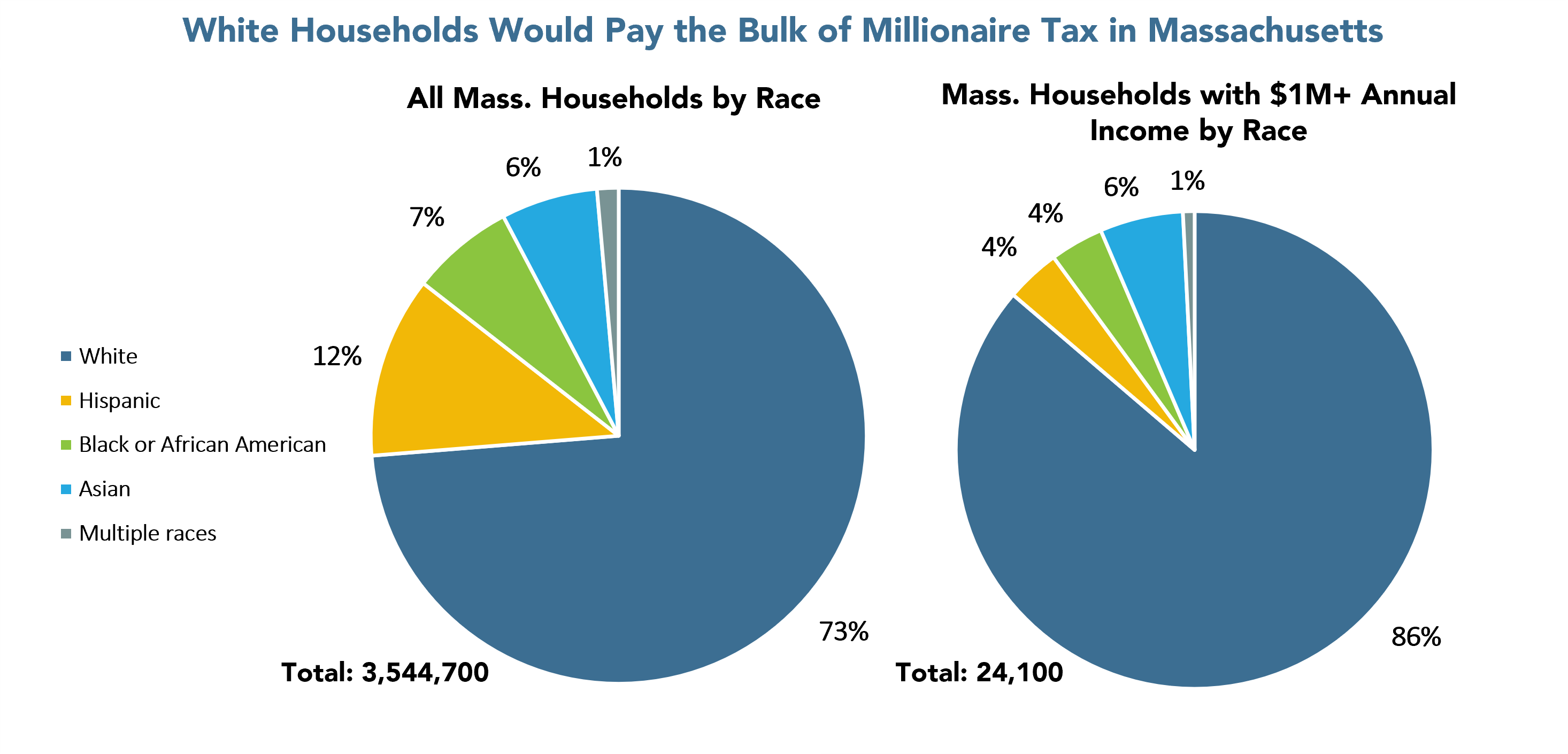
In fact, it is likely that these white households would pay more than 86 percent of the total tax, because these few, very high-income white households likely have higher incomes, on average, than do the very high-income Black and brown households that would be subject to the surtax. Because these white households likely receive more than 86 percent of the income subject to the surtax, they would contribute more than 86 percent of the total revenue collected through a millionaire tax.
It also is the case that a slightly higher percentage of all white households in Massachusetts would be subject to the tax than the percentage of all Black, brown or Asian households that would be affected – though well less than 1 percent of all Massachusetts households would be subject to the tax (see table below).
| Only A Very Small Percent of MA Households Would Pay Millionaire Tax | ||
|---|---|---|
| Racial Group | Percent of Households That Would Pay Millionaire Tax | Number of Households That Would Pay Millionaire Tax |
| White | 0.8% | 20,700 |
| Asian | 0.6% | 1,400 |
| Multiple Races | 0.4% | 200 |
| Black or African American | 0.4% | 900 |
| Hispanic | 0.2% | 900 |
| Statewide | 0.7% | 24,100 |
It is important to underscore that every household affected by a millionaire tax, regardless of race, would be a household that enjoys very high-income. Each of these households – white, Black or brown – would have annual income of more than $1 million a year. And income is not the same as wealth. A “millionaire tax” would not apply to the many kinds of wealth that people may hold. The tax would not apply to bank accounts, retirement funds, stock portfolios or the wealth people hold in the value of their houses and businesses. A millionaire tax would apply only to the portion of household income that exceeds $1 million in any given year.





